How Ayurveda treated this diseases 3000 years before
Why Allopathy Struggles With Recurrence
MODERN RESEARCH & ITS RESULTS
Kidney stones have troubled humans for thousands of years, with Ayurveda offering one of the earliest holistic approaches to diagnosis and management, focused on natural and gentle methods rather than invasive surgery.
Even today, recurrence after allopathic surgery is common, making ancient strategies especially relevant.
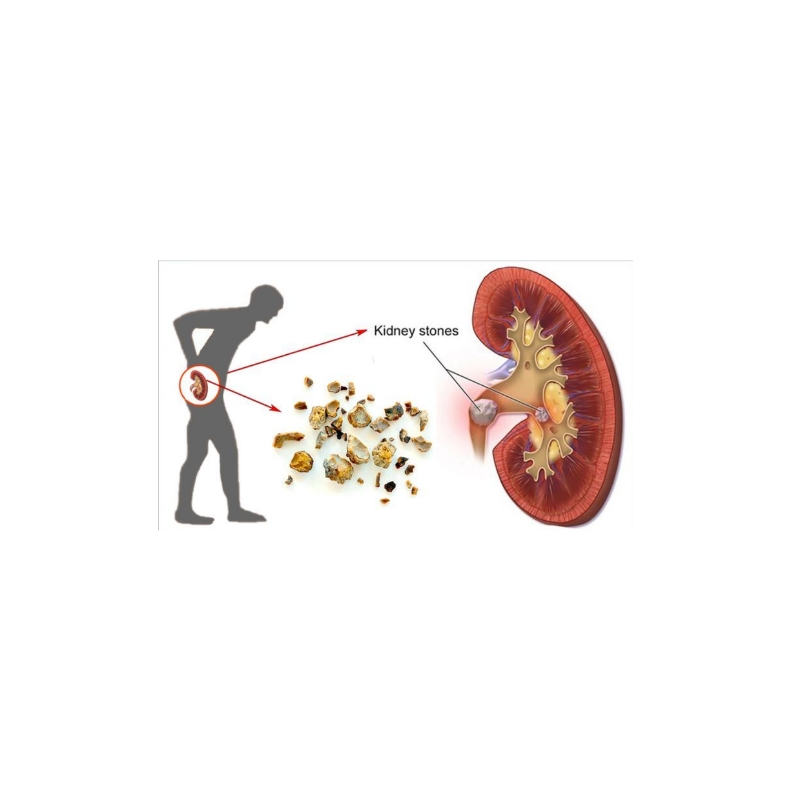
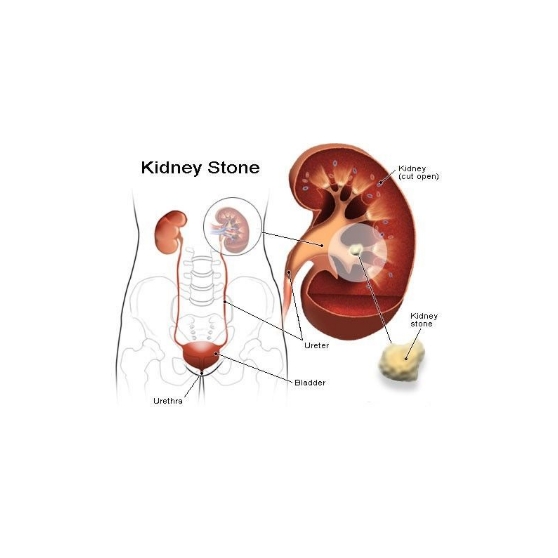
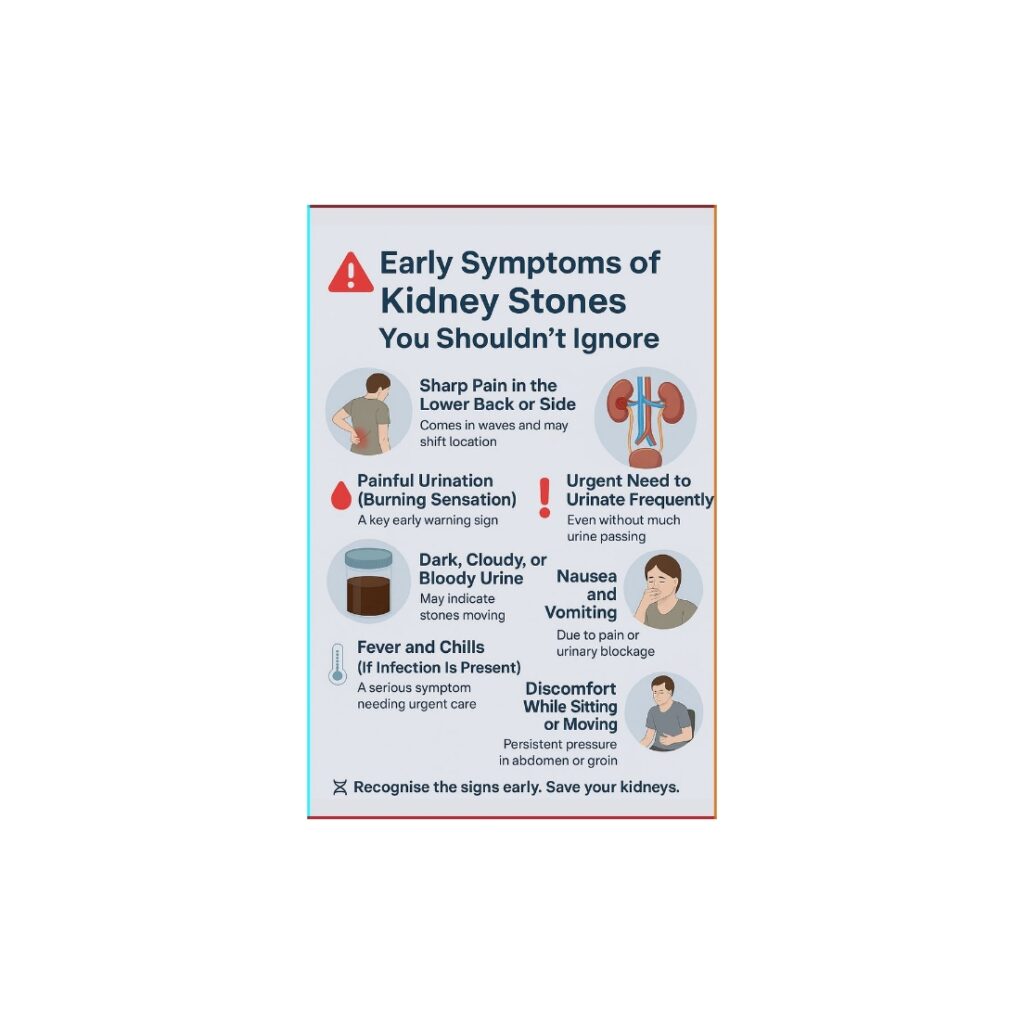
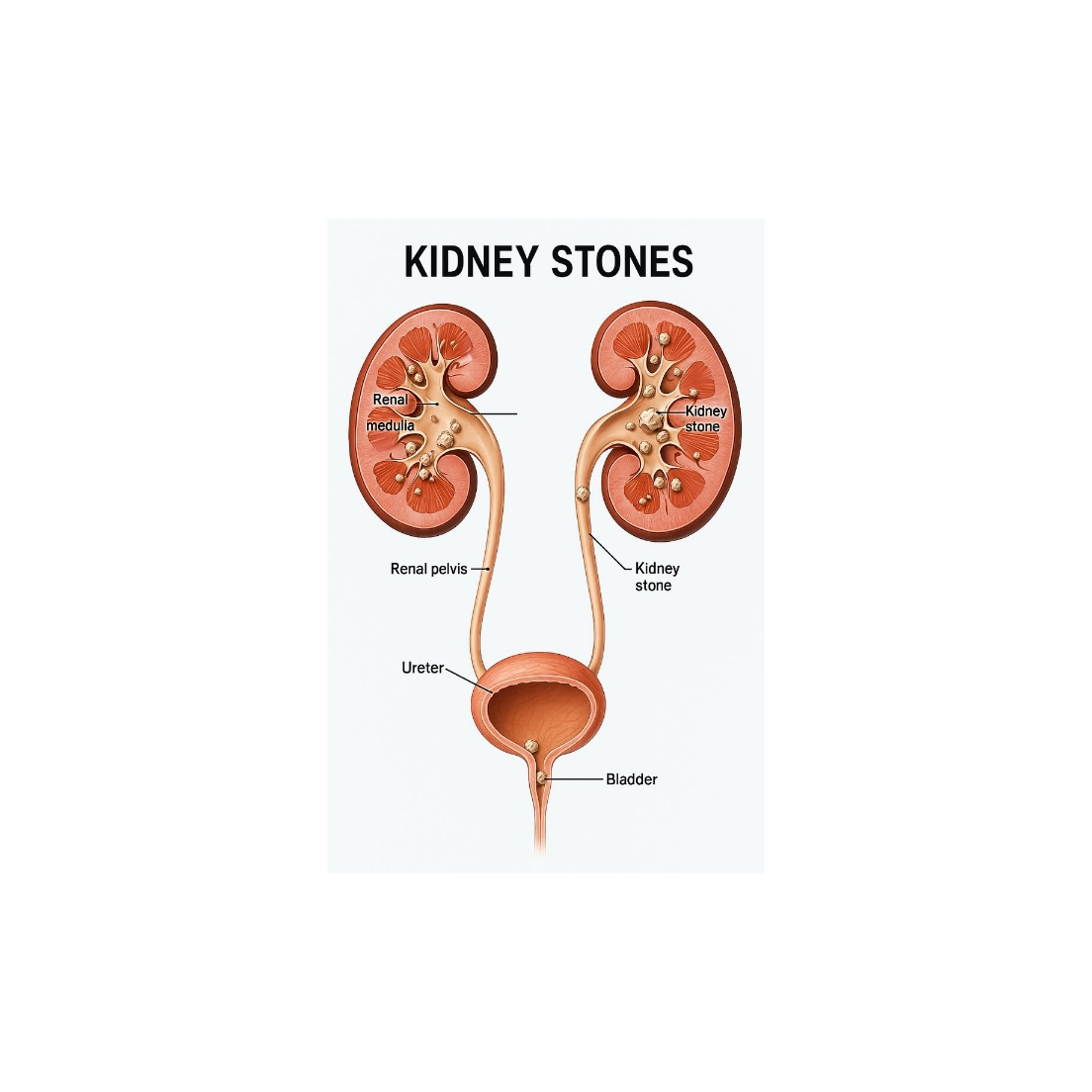
How Kidney Stones Form
Kidney stones develop when minerals like calcium, oxalate, or uric acid crystallize and clump together in the urinary system
Factors such as dehydration, imbalanced diet, genetic predisposition, chronic infections, and medicines can contribute.
Ayurveda describes this as an imbalance in the body’s doshas that leads to crystallization of waste (‘Mutrashmari’ in Sanskrit
. After surgery—if underlying factors like diet, hydration, or metabolic imbalance remain—the risk of new stones stays high; recurrence rates after surgery are 30–50% within five years
Ancient Ayurvedic Treatment Method
Ayurveda rarely used invasive surgery for stones. Instead, it relied on specialized therapies and herbal formulations:
Viddha Karma (Needling): As described by Sushruta, this technique involves stimulating specific points (often lateral border of the thumb or leg) to promote movement and elimination of stones through the urinary tract—akin to acupuncture, but focused on improving ureter motility
Shamana Chikitsa (Pacification Therapy):
Herbal medicines like Chandraprabha Vati, Varunadi Kashaya, and Gokshura were used to dissolve stones, reduce inflammation, and improve urinary flow. Other herbs such as Punarnava, Palash, and Pashanbheda act as diuretics or stone-dissolvers
Diet and Lifestyle
Patients were advised to drink plenty of water, reduce sodium/protein, and follow a kidney-friendly diet of whole grains, leafy vegetables, and fruits. Detoxification therapies (Virechana, Basti, Swedana) were used to purge toxins and reduce recurrence
Recurrence and Modern Insights
– Stones often return after surgery because only the stone—not the causative metabolic or lifestyle factor—is removed
In Ayurveda, both the tendency (“beeja dosha”) and the substrate (“kleda”) must be treated.
– Recent research shows composition plays a big role: patients with uric acid, calcium phosphate, or cystine stones may have quicker or more frequent recurrences than those with calcium oxalate stones
– Ayurveda’s focus on regular detox, personalized diet, and herbal support helps address root causes rather than symptoms, potentially reducing recurrence
Why Allopathy Struggles With Recurrence
Allopathy excels at fast, safe removal via surgery (lithotripsy, nephrolithotomy) but often lacks lasting solutions without dietary/modification follow-up
Despite surgery, factors like high urinary calcium, persistent infection, or metabolic conditions often remain unaddressed, leading to new stones New research includes advanced imaging, stone composition analysis, and even robotic ultrasound for moving fragments, lowering recurrence risk
Ayurvedic Remedies to Prevent Recurrence
– Herbal formulations: Varunadi Kwath, Gokshura, Pashanbheda, Chandraprabha Vati, Ren-Cit Cystone help dissolve and clear crystals, strengthen kidney health, and promote urinary flow
– Therapy: Virechana (purgation) and Basti (medicated enema) clear toxins and rebalance doshas
– Diet: Advocates hydration, low-protein/salt intake, and supportive foods (barley, millet) – Lifestyle: Consistent hydration, physical activity, and avoidance of excess antacids or protein diet
Latest Research Insights
– Stone recurrence has strong links to stone composition, underlying metabolic issues, persistent infections, and incomplete removal of fragments
– Non-invasive therapies like targeted ultrasound to push stone fragments and improved metabolic evaluations show promise in reducing recurrence
– Prevention via dietary and metabolic management is critical, echoing Ayurvedic principles
Summary
The journey from Ayurveda to modern medicine shows that kidney stone treatment is most effective when addressing not just the symptoms (the stone itself) but the underlying physiology, diet, and lifestyle. Ancient non-surgical techniques like Viddha Karma and herbal remedies may offer a blueprint for safer, longer-lasting care. Even today, blending these with modern diagnostics could help prevent stones from coming back—a goal as important as their removal.



Easy representation of important knowledge for every age
Nicely , explained how stones form, why it reoccurs, ….and treatment management in a logner run..👍👍🙏🙏
Nice