Diseases Common in Older Adults (Age 60–85): Causes, Stomach Problems, and Why Many Seniors Stoop While Walking
Meta Description:
A simple‑ guide explaining common diseases in older adults (60–85 years), why stomach problems are frequent, and why many seniors stoop while walking. Includes causes, prevention tips, and SEO‑optimized headings.
Alt Text Old age various diseases
Keywords:
Diseases in old age, senior health problems, stomach issues in elderly, stooped posture in old age, ageing diseases India, health problems age 60 to 85, chronic diseases elderly, digestive issues seniors, osteoporosis posture problems.
Introduction
As people grow older, their bodies naturally change. Organs slow down, bones become weaker, digestion becomes less efficient, and immunity drops. According to global health data, most adults above 65 have at least one chronic disease, and many have two or more. The World Health Organization also reports that the number of older adults is increasing rapidly worldwide.
This article explains the common diseases in people aged 60–85, why stomach problems are frequent, and why many seniors stoop while walking. The language is simple so that families, caregivers, and older adults can easily understand.
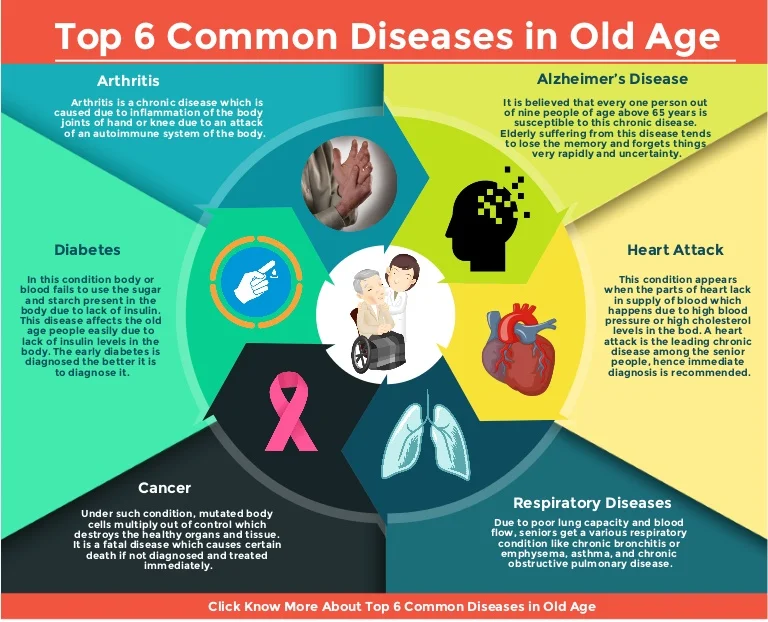
Common Diseases in Older Adults (Age 60–85)
Research shows that older adults are more likely to develop chronic diseases because the body’s repair system becomes slower with age. Here are the most common conditions:
1. High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)
Very common in older adults. Blood vessels become stiff, making the heart work harder.
Symptoms: Headache, dizziness, tiredness.
Risks: Stroke, heart attack.
2. Diabetes (Type 2)
Age reduces insulin efficiency, and metabolism slows down.
Symptoms: Frequent urination, thirst, weakness.
Risks: Kidney disease, nerve damage, vision loss.
3. Heart Disease
Includes blocked arteries, heart failure, and irregular heartbeat.
Symptoms: Chest pain, breathlessness, swelling in legs.
4. Arthritis and Joint Pain
Cartilage wears down with age, causing pain in knees, hips, and fingers.
Symptoms: Stiffness, swelling, difficulty walking.
5. Osteoporosis (Weak Bones)
Bones become thin and fragile, especially in women after menopause.
Symptoms: Back pain, fractures, stooped posture.
6. Digestive Problems
Very common in older adults due to slow digestion and weak gut muscles.
Symptoms: Gas, bloating, constipation, acidity.
7. Lung Diseases (COPD, Asthma)
Lung capacity decreases with age.
Symptoms: Breathlessness, cough, wheezing.
8. Kidney Problems
Kidneys lose filtering power with age.
Symptoms: Swelling, fatigue, changes in urination.
9. Vision Problems (Cataract, Glaucoma)
Eyes become cloudy or pressure increases.
Symptoms: Blurred vision, difficulty reading.
10. Hearing Loss
Ear nerves weaken over time.
Symptoms: Difficulty hearing conversations.
11. Memory Loss and Dementia
Brain cells shrink with age.
Symptoms: Forgetfulness, confusion, mood changes.
12. Depression and Anxiety
Loneliness, illness, and loss of independence can affect mental health.
13. Urinary Problems
Weak bladder muscles cause frequent urination or leakage.
14. Skin Problems
Dry skin, itching, infections due to thin skin.
15. Immune System Weakness
Older adults catch infections more easily.
Why Older People Frequently Suffer Stomach Diseases
Stomach and digestive issues are extremely common in people aged 60–85. There are several reasons:
1. Slow Digestion
With age, the digestive system becomes slow. Food stays longer in the stomach, causing:
– Gas
– Bloating
– Acidity
– Constipation
2. Weak Digestive Muscles
The muscles of the intestine lose strength, making bowel movement slow.
3. Low Stomach Acid
Older adults produce less stomach acid, which affects digestion of proteins and vitamins.
4. Medications
Many seniors take medicines for BP, diabetes, heart disease, etc.
These medicines can irritate the stomach.
5. Poor Gut Bacteria Balance
Age reduces healthy gut bacteria, leading to:
– Indigestion
– Constipation
– Infections
6. Dehydration
Older adults often drink less water, causing constipation.
7. Less Physical Activity
Lack of movement slows digestion.
8. Chronic Diseases
Diabetes, thyroid problems, and kidney disease affect digestion.
Why Older People Stoop While Walking
Many people between 60 and 85 develop a stooped posture. This is usually due to:
1. Osteoporosis (Weak Bones)
Bones become thin and fragile.
The spine becomes weak and bends forward.
2. Muscle Weakness
Back and core muscles lose strength with age.
Weak muscles cannot support the spine properly.
3. Arthritis of the Spine
Joints in the spine become stiff and painful, causing bending.
4. Disc Degeneration
Spinal discs shrink with age, reducing height and causing stooping.
5. Poor Posture Over Many Years
Long-term habits like:
– Sitting hunched
– Working at desks
– Lack of exercise
…lead to a bent posture in old age.
6. Parkinson’s Disease
Some neurological conditions cause forward bending.
7. Vitamin D and Calcium Deficiency
Weak bones and muscles contribute to stooping.
How Families Can Help Older Adults Stay Healthy
Here are simple steps to reduce disease risk:
1. Encourage Daily Walking
Improves digestion, heart health, and posture.
2. Give a Balanced Diet
Include:
– Fruits
– Vegetables
– Whole grains
– Protein
– Calcium-rich foods
3. Ensure Adequate Water Intake
Prevents constipation and dehydration.
4. Regular Health Checkups
Early detection prevents complications.
5. Strengthening Exercises
Light exercises for back and leg muscles help prevent stooping.
6. Vitamin D and Calcium Supplements
Only under doctor guidance.
7. Reduce Stress and Loneliness
Family time, hobbies, and social interaction improve mental health.
Conclusion
Ageing is a natural process, and with it come several health challenges. Adults aged 60–85 commonly face diseases like hypertension, diabetes, arthritis, digestive issues, and bone weakness. Stomach problems occur because digestion slows down, and stooping happens due to weak bones, muscles, and spine changes.
With proper care, nutrition, exercise, and regular checkups, older adults can live healthier, happier, and more active lives.
Disclaimer
This article is for educational purposes only. It is not a substitute for medical advice. Always consult a qualified doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
Sources
– National Council on Aging – Chronic diseases in older adults
– World Health Organization – Ageing and health facts
– Chapter Medicare – Common medical conditions in older adults
Internal link learn more from similar articles on https://dailydrdose.com





