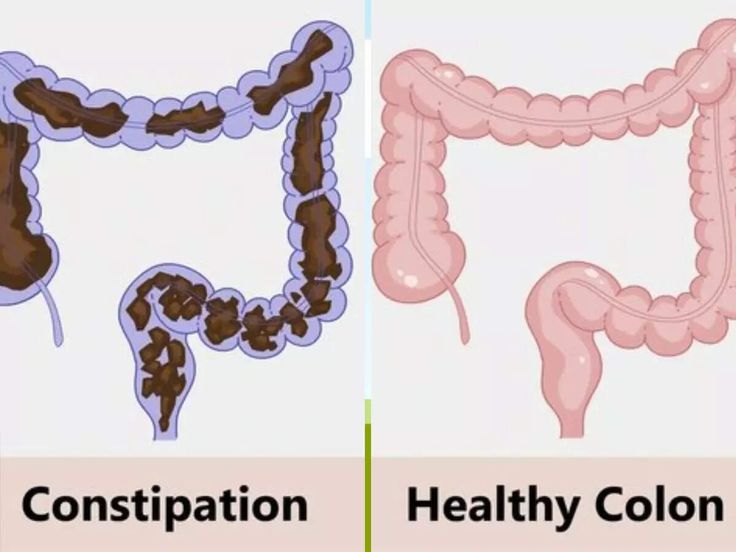

Think of your digestive system as a pipeline. Food goes in at one end (mouth), nutrients are absorbed along the way, and waste comes out at the other end (anus).Constipation is when the waste material (stool) moves too slowly through the pipeline, becoming hard, dry, and difficult to pass.
Small Intestine vs. Large Intestine:
constipation is primarily a large intestine (colon) issue not the small intestine.The small intestine’s job is to absorb nutrients. The colon’s job is to absorb water from the waste. If the waste stays too long in the colon, too much water is absorbed, making it hard and dry.
Main Causes of Constipation:
* Diet: Lack of fiber (fruits, vegetables, whole grains) and insufficient water intake.
* Lifestyle:Lack of physical activity (movement helps the intestines move).
* Habits: Ignoring the urge to go to the toilet.
* Medications: Some painkillers, antacids, etc.
* Stress and Anxiety:The gut and brain are directly connected (gut-brain axis).
The Constipation-Piles Connection: The Domino Effect
This is a perfect example of a domino effect.
1. Chronic Constipation: You strain hard to pass hard stools.
2. increased Pressure: This straining creates immense pressure in the veins of the lower rectum and anus (similar to how pressure builds in a blocked water hose).
3. Veins Swell: These veins, called “anal cushions,” are normal tissue that help with stool control. Under constant pressure, they swell up, stretch, and bulge, forming piles (hemorrhoids).
* Internal Piles: Swollen veins inside the rectum. Can cause bleeding.
* external Piles: Swollen veins under the skin around the anus. Can be painful and itchy.
Note on Portal Vein Blockage:
Portal vein hypertension is a serious liver disease that can cause ascites (fluid in the abdomen) and hemorrhoids, but it is not the common cause of piles for most people. The common culprit for the general population is chronic constipation and straining.
Modern Medicine (Allopathy) Diagnosis & View
Diagnosis:
A doctor (proctologist) will typically:
1. Physical Examination: Look at the anal area.
2. Digital Rectal Exam (DRE): Use a gloved, lubricated finger to feel for abnormalities.
3. Anoscopy/Proctoscopy :Use a short, lighted tube to look inside the anus and rectum.
Allopathic View on Ayurveda/Herbal Medicine:
* Allopathy is a science-based system. It requires treatments to be proven through large-scale, repeatable clinical trials.
* Many allopathic doctors are skeptical of Ayurvedic and herbal remedies because the evidence from such trials is often limited or inconsistent. They worry about:
* Lack of Standardization: The potency of an herb can vary greatly.
* Potential Side Effects & Interactions:
Some herbs can interact dangerously with prescription medicines or contain toxic heavy metals if not prepared properly. So, they don’t so much call it “inappropriate” as they call it “unproven” or “potentially risky.” Their advice to “avoid altogether” is a cautionary stance to prevent harm.
Surgery as Last Resort:
Surgery (like hemorrhoidectomy) is indeed the last option for large, painful, or bleeding piles that don’t respond to other treatments. While success rates are very high (much higher than 1%), complications like pain or recurrence can happen, which is why it’s not the first choice.
Ayurvedic Perspective and Home Remedies
Ayurveda sees constipation (*Vibandha*) as an imbalance of the *Vata* dosha (the air and space element), which governs movement.
Root Cause in Ayurveda: Weak digestive fire (*Agni*), poor diet, and stress leading to *Vata* imbalance.
Home Remedies & Herbal Medicines (Always consult an Ayurvedic practitioner first):
* Diet & Lifestyle:
* Triphala: The most famous Ayurvedic remedy. A powder of three fruits taken with warm water at bedtime. It gently cleanses and regulates the bowels.
* Ghee (Clarified Butter): 1-2 teaspoons in warm milk or water. Lubricates the intestines.
* Warm Water: Sip warm water throughout the day to pacify Vata.
* High-Fiber Diet: Figs, prunes, psyllium husk (*Isabgol*).
* Herbs: *Haritaki*, *Trivrut*, *Guggulu*, *Castor Oil* (in specific doses).
Homeopathic Approach
Homeopathy works on the principle of “like cures like” – using highly diluted substances that in large doses would cause symptoms similar to the disease.
Role of Homeopathy: It aims to stimulate the body’s own healing response. The medicine is chosen based on the individual’s unique symptoms.
Common Homeopathic Medicines for Piles (Must be prescribed by a homeopath):
* Aesculus hippocastanum: For piles with a burning, dry feeling and backache. Feeling of sticks in the rectumHamamelis virginiana:** For bleeding piles with soreness and a feeling of bruising.
* Nux vomica:For piles in sedentary people who suffer from constipation due to spicy food, coffee, and stress. Constant but ineffective urge to pass stool.
* Sulphur: For burning, itching piles that are worse with heat and washing.
* Aloe socotrina: For piles that look like a bunch of grapes, often better with cold water application.
Siddha Medicine: The “Upper Hand”?
Siddha is a traditional system from Tamil Nadu, India, similar to Ayurveda but with its own unique philosophies and preparations, often using metals and minerals in processed forms.
Why some believe it has an “upper hand”
* Its proponents believe Siddha medicines are very potent and act faster for certain conditions, including piles, due to the use of *parpam* and *chendooram* (processed mineral formulations).
* It is deeply rooted in Tamil culture, and strong cultural belief can contribute to the perceived effectiveness.
The claim that one system has an “upper hand” over all others is subjective. What works miraculously for one person may not work for another. The best system is often the one that is **safe, evidence-informed, and works for you under proper guidance.
Summary for a Layman: Key Takeaways
- Prevention is Key:
The real culprit is often a poor diet and lifestyle. **Eat more fiber, drink more water, and exercise regularly.**
- Don’t Strain:
- Listen to your body. Go when you feel the urge.
Modern Medicine is Effective for Diagnosis:
If you have a serious problem, see a doctor for a proper diagnosis to rule out other condition
- Respect All Streams, but be Cautious:
Ayurveda, Homeopathy, and Siddha have their own strengths and dedicated followers. They can be very helpful. However, always consult a qualified, registered practitioner in any system. Do not self-medicate.
5 Surgery is a Last Resort: It has a high success rate but is reserved for severe cases.
The goal is not to prove one system superior, but to be aware of the options and approach our health in an informed, balanced way.
Always keep your primary healthcare provider informed about any other treatments you are taking.
Warning :This blog is only for health awareness not for any diagnosis and others

It’s really superb
Great knowledge provided sir
बहुत अच्छी जानकारी दी सर आपनेट पित और कब्ज को लेकर पाचन क्रिया का पूरा विश्लेषण किया और बवासीर का भी आपने बताया खाने में सुधार और उचित मात्रा में पानी को पीना चाहिए यह जानकारी हम अपने परिवार में सबको बताएंगे खान-पान अच्छा रहेगा तो हम इंसान स्वस्थ रहेंगे धन्यवाद सर।
Great 👍🏻😃
Nice