

Introduction: Why Obesity Is More Than Just Weight Gain
Obesity is not simply a matter of excess fat—it’s a complex, chronic condition that disrupts nearly every system in the human body. From hormonal glands to vital organs and joints, obesity triggers a cascade of disorders that silently erode physical and mental health. In India and globally, rising obesity rates are linked to lifestyle changes, urban diets, and stress-driven hormonal shifts.
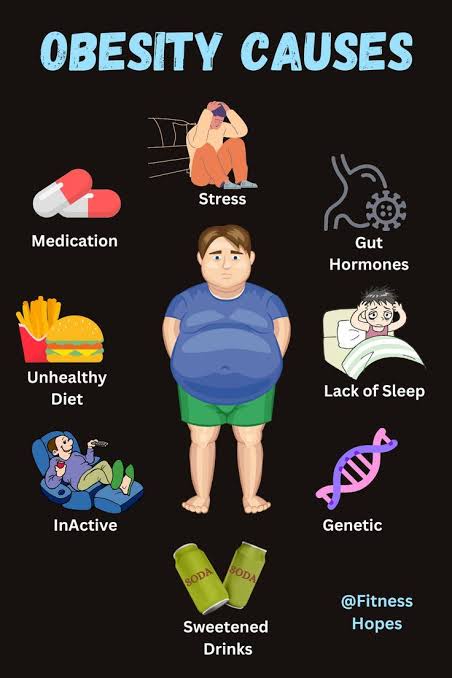
🔍 What Causes Obesity?
Obesity arises from a mix of biological, behavioral, and environmental factors:
– Caloric imbalance: Consuming more calories than burned
– Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of physical activity
– Hormonal disruptions: Insulin, leptin, ghrelin, and cortisol imbalances
– Genetic predisposition: Family history of obesity or metabolic disorders
– Psychological stress: Chronic stress elevates cortisol, promoting fat storage
– Sleep deprivation: Alters hunger hormones and metabolism
🧬 Hormonal Glands & Obesity: The Invisible Drivers

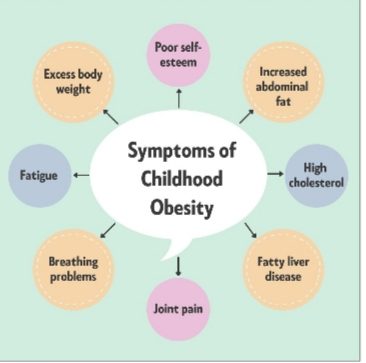

Obesity deeply affects the endocrine system, disrupting hormonal balance:
| Hormone | Function | Obesity Impact |
Insulin | Regulates blood sugar | Insulin resistance leads to fat storage & type 2 diabetes |
| Leptin | Signals fullness | Leptin resistance causes overeating despite full fat stores |
| Ghrelin | Stimulates hunger | Elevated ghrelin increases appetite & weight gain |
| Cortisol | Stress response | High cortisol promotes belly fat & metabolic syndrome |
🫀 Major Organs Under Attack
Obesity doesn’t just sit under the skin—it infiltrates organs and disrupts their function:
❤️ Heart
– Increased risk of hypertension, heart failure, and stroke
– Fat buildup around arteries leads to atherosclerosis
🧠 Brain
– Inflammation affects memory, learning, and emotional regulation
– Higher risk of depression and cognitive decline
🫁 Lungs
– Reduced lung capacity and sleep apnea
– Fat around the chest restricts breathing
🍽️ Liver & Pancreas
– Fatty liver disease and insulin resistance
– Increased risk of type 2 diabetes
🦴 Joints
– Excess weight strains knees, hips, and spine
– Accelerates osteoarthritis and joint degeneration
🧠 Mental Health & Obesity: A Vicious Cycle
Obesity and mental health are tightly linked. Emotional eating, body image issues, and hormonal shifts contribute to:
– Depression
– Anxiety
– Low self-esteem
– Social withdrawal
Prevention & Public Awareness: What You Can Do
Empowering communities with knowledge is key. Here’s how we can fight obesity:
– Educate: Share bilingual resources on nutrition and exercise
– Engage: Promote physical activity in schools and local events
– Empathize: Address emotional and psychological roots of obesity
– Equip: Provide access to healthy food and mental health support
Final Thoughts: Obesity Is Treatable, Awareness Is Powerful
Obesity is not a personal failure—it’s a systemic challenge. By understanding its causes and effects, we can build healthier communities. Let’s turn knowledge into action, compassion into reform, and awareness into healing.
Major Organ Disorders Due to Obesity
1. Cardiovascular System
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Atherosclerosis (narrowing of arteries)
- Coronary artery disease (angina, heart attack)
- Congestive heart failure
- Arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats)
- Stroke
2. Respiratory System
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Hypoventilation syndrome (“Pickwickian syndrome”)
- Asthma worsening
- Reduced lung capacity
3. Liver & Digestive System
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
- Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH → can progress to cirrhosis)
- Gallstones
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Colon cancer risk ↑
4. Kidneys & Urinary System
- Obesity-related glomerulopathy (damage to kidney filters)
- Increased risk of kidney stones
- Chronic kidney disease
5. Nervous System
- Increased risk of stroke
- Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (“pseudotumor cerebri”)
- Peripheral neuropathy (indirect, via diabetes)
🦴 Joints Largely Affected by Obesity
- Knee joints → osteoarthritis (most common, due to weight-bearing stress)
- Hip joints → degeneration and arthritis
- Spine (lumbar region) → chronic back pain, disc disease
- Ankles & feet → plantar fasciitis, flat feet strain
Excess weight accelerates cartilage wear and leads to chronic inflammation around joints.
🧬 Hormonal & Metabolic Disorders Due to Obesity
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (insulin resistance)
- Metabolic syndrome (abdominal obesity, high BP, high sugar, high triglycerides, low HDL)
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) in women
- Hypogonadism in men (low testosterone)
- Thyroid dysfunction (mostly subclinical hypothyroidism aggravated by obesity)
- Leptin resistance (appetite control hormone dysfunction)
- Cortisol imbalance (increased stress hormone)
- Increased risk of certain cancers (breast, colon, endometrial, pancreatic) due to hormonal imbalances
✅ In summary:
Diabetes, PCOS, thyroid, testosterone deficiency are key hormonal disorders.
Heart, liver, kidneys, lungs, brain are major organs affected.
Knees, hips, spine are the main joints damaged.




👍